Neptune is big, it’s blue, and it is a planet that can tear you apart if you happen to drop into one of its massive, Earth-sized storms. While it might look calm and breathtaking from afar, Neptune is one of the most violent places in our solar system. Its deep blue color comes from methane in the atmosphere, which absorbs red light and reflects blue, giving the planet its striking appearance.
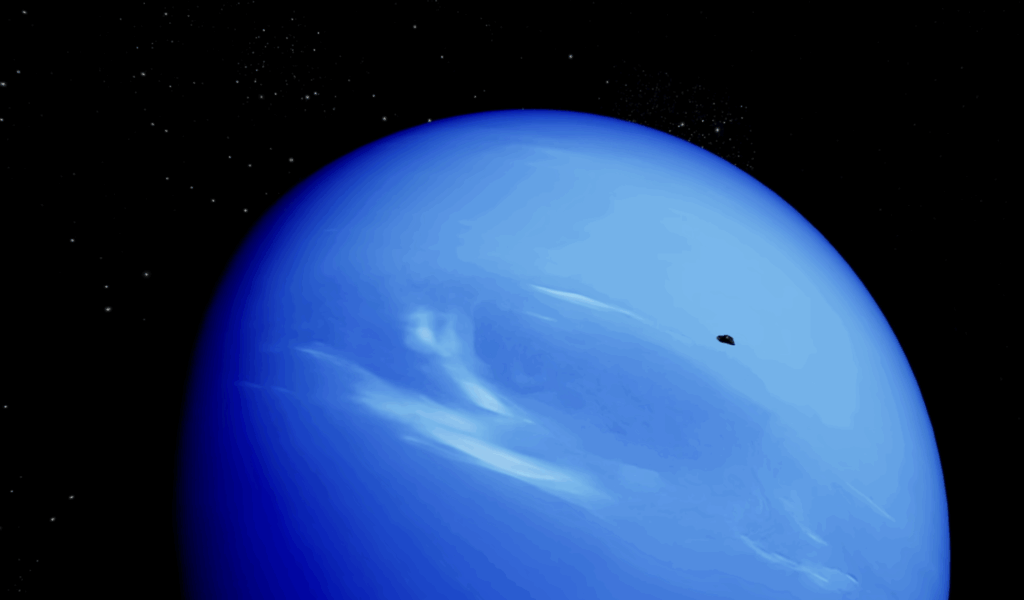

Despite being so far from the Sun, Neptune has the strongest winds of any planet, making its surface a place of extreme and unpredictable weather. If you’re dreaming of a cosmic adventure, here are five things you should know before taking the plunge.
1. The Dark Spots Are Dangerous Storms
Neptune is famous for its dark spots, including the legendary Great Dark Spot, which once raged with the power to contain the entire Earth. Though the original storm has dissipated, smaller but still violent storms continue to whip across the planet. Wind speeds can reach a staggering 550 meters per second, about five times stronger than the harshest gusts on Earth and twice the speed of sound.
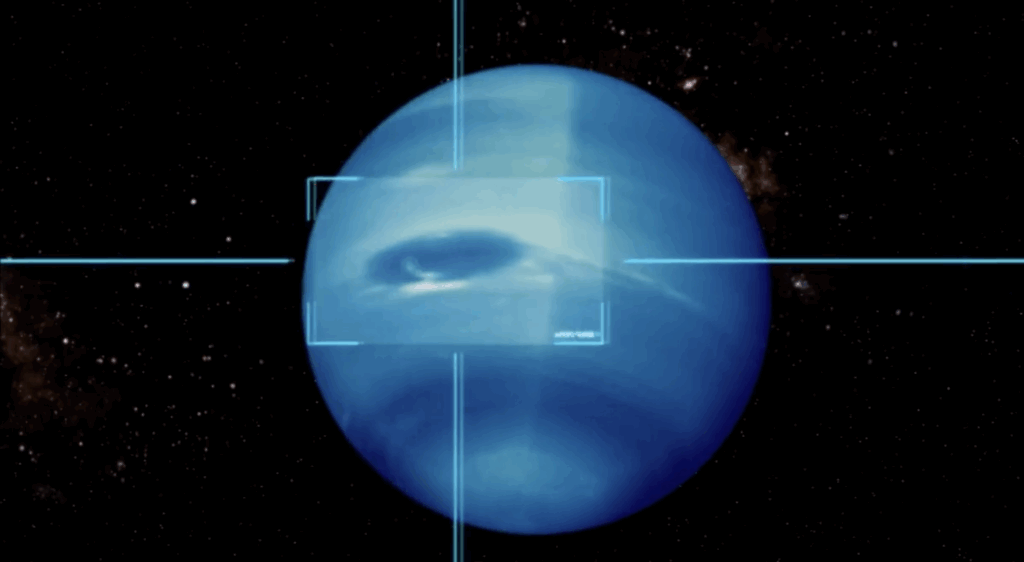
These storms can move incredibly fast, shifting the planet’s weather patterns in just a matter of hours. The northern hemisphere is generally calmer, making it the best place to survive a descent. Even here, however, explorers would have to contend with constant turbulence and swirling clouds that could knock spacecraft off course.
2. Its Rings and Moons Are Full of Mysteries
Neptune has an intricate ring system, although not as extensive as Saturn’s. The planet’s rings contain clumps of dust called arcs, which astronomers believe are influenced by the gravitational pull of Neptune’s moon Galatea. Beyond its rings, Neptune boasts 14 moons, with Triton being the most famous for its spectacular ice volcanoes.
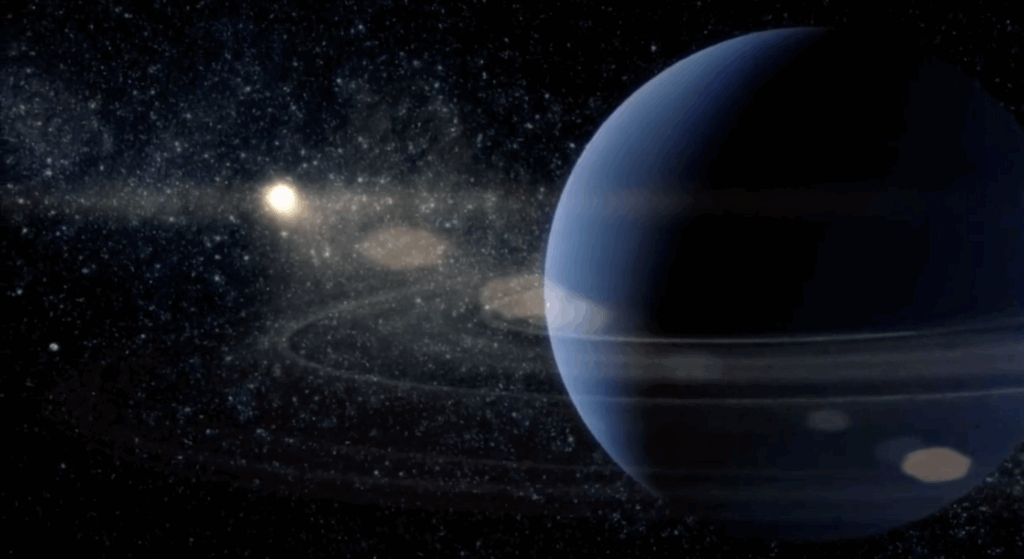
Triton is unique because it orbits Neptune in the opposite direction of the planet’s rotation, a phenomenon known as a retrograde orbit, which suggests it may have been captured from the Kuiper Belt. The complex interactions between the planet and its moons create a dynamic and mysterious environment in orbit. Studying these moons could reveal clues about the formation of the outer solar system and the forces that shape planetary systems.
3. The Atmosphere Is Deadly for Humans
Neptune’s atmosphere is mostly hydrogen, helium, methane, and ammonia, with no oxygen to breathe. Temperatures fluctuate wildly, from freezing cold in the outer exosphere to scorching heat of nearly 477 °C in the thermosphere. The atmosphere also contains high clouds of methane ice that can reflect sunlight, making some areas slightly brighter than others despite the planet’s distance from the Sun.
As you descend deeper, pressure increases dramatically, and the dense atmosphere makes it nearly impossible to see anything. Survival requires specialized equipment capable of withstanding extreme cold, high winds, and toxic clouds. Any human mission would need advanced life support systems and protective shielding against the planet’s constant electrical storms and radiation bursts.
4. The Core Holds Hidden Treasures
Beneath Neptune’s 3,000 kilometer thick atmosphere lies a slushy layer of ice and water, followed by a superhot ocean and a dense core. High pressure and temperature could squeeze carbon atoms into diamonds as large as one meter, which then sink toward the planet’s core. Scientists believe this process creates a kind of “diamond rain,” producing massive quantities of precious stones that could exist in solid layers deep below the surface.
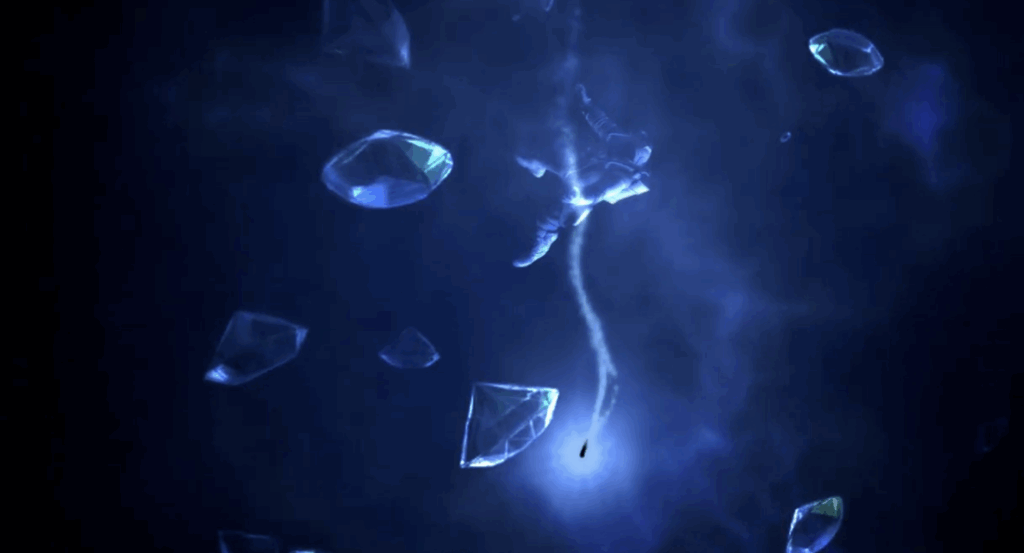
This means Neptune may be hiding massive deposits of diamonds, a glittering secret buried deep beneath the storms and clouds. Studying these layers could also provide insights into exotic chemical reactions that are impossible on Earth, offering a window into planetary physics at its most extreme.
5. Human Survival Is Nearly Impossible
With surface conditions that range from hurricane force winds to extreme temperatures and pressures, a human could not survive on Neptune. Even a resilient space probe would face challenges navigating through the methane clouds, ammonia storms, and hydrogen and helium layers. The core temperature of about 7,000 °C rivals the surface of the Sun, underscoring that Neptune is a realm for scientific exploration rather than tourism. Even sending robotic explorers is risky, as materials would need to withstand crushing pressures and extreme corrosion from the planet’s volatile gases. For now, Neptune remains a place for observation and remote study, far beyond the reach of human hands.

Neptune is a planet that captures the imagination, from its violent storms to its hidden treasures. While humans may never walk its surface, the mysteries it holds continue to inspire scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Its extreme conditions make it a laboratory for understanding the limits of physics and the behavior of matter under pressure. As we explore further into the solar system, Neptune remains a reminder of the extreme forces and breathtaking wonders that lie beyond Earth. Its storms, rings, moons, and hidden diamond oceans make it a planet that challenges our imagination and pushes the boundaries of what we know about the universe.