We think of space as an icy void, where temperatures drop to hundreds of degrees below zero and astronauts need layers of thermal protection just to survive. But what if everything flipped? What if space, once frigid and hostile, suddenly became scorching hot?
This wild thought experiment opens the door to some surprising science. It challenges our basic understanding of the Universe and pushes the limits of what we think is possible. Here are seven facts that explore what would happen if outer space suddenly turned up the heat.
1. Space Is Cold Because It Is Mostly Empty
Space is not cold just because it is far from the Sun. It is cold because it is almost entirely empty. With so few particles floating around, there is almost no matter to absorb or transfer heat. This means there is nothing to hold warmth, even in the presence of powerful stars.

The average temperature of the Universe sits at a chilling 2 point 7 degrees Kelvin, which is about minus 270 degrees Celsius. That is nearly as cold as physics allows. What little warmth exists comes from something called the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation, a leftover echo from the Big Bang itself.
Without that ancient radiation, the temperature of deep space would be even closer to absolute zero, making it completely inhospitable to any form of life or machine.
2. Heating Up Space Would Require Major Cosmic Changes
To make space warmer, you would need to introduce more energy on a massive scale. That does not mean just adding a few more campfires. We are talking about monumental events like a supercharged Sun or the emergence of new energy sources throughout the Universe.

Without a dense medium to transmit heat, most of the new warmth would only affect areas around stars and planets where matter is more concentrated. Empty regions would still remain chilly. To truly heat space, you would need to change the fabric of the Universe itself. That would require altering the very physics of matter and energy distribution, something well beyond our current scientific capabilities.
3. A Hotter Sun Would Make Earth Unlivable
The most local way to raise the temperature in space would be to supercharge our Sun. If the Sun were to become a Red Giant, it would expand dramatically and release far more heat and radiation. But that kind of increase would be disastrous for Earth. It would trigger a runaway greenhouse effect, where the planet’s atmosphere traps more and more heat.
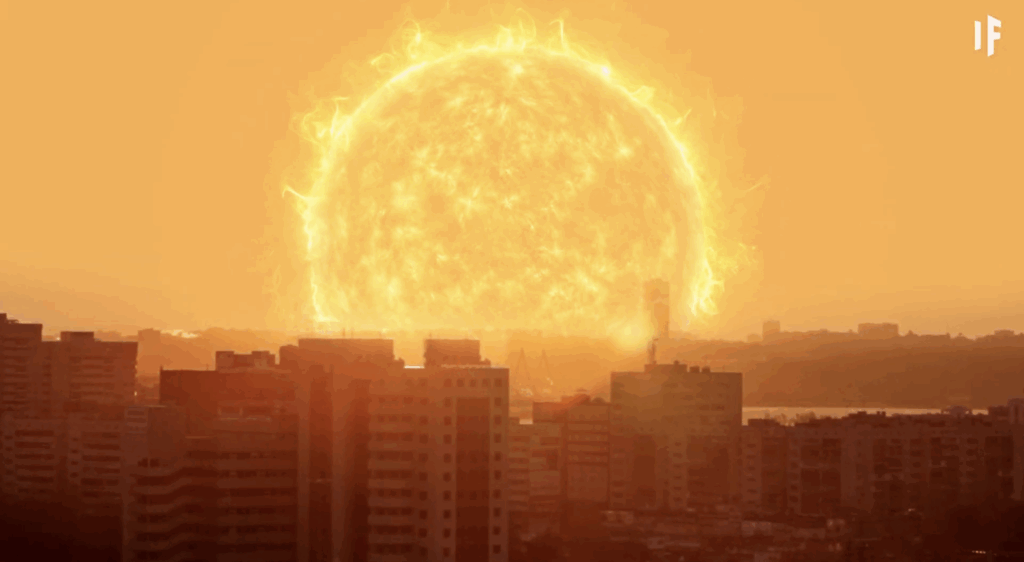

Eventually, this would boil the oceans, scorch the land, and leave Earth as a lifeless husk. Not to mention, the Sun would grow so large that it could engulf Earth entirely. Temperatures would soar to levels that no current technology or shelter could withstand. Life as we know it would be doomed within a matter of years or even months.
4. Filling the Galaxy With More Stars Could Do the Trick
If changing one Sun is not enough, what about adding billions of new ones? The Milky Way currently contains up to 400 billion stars, but they are spaced very far apart. If we doubled that number and packed them closer together, we might raise the ambient temperature of space slightly. Especially if those new stars were blue giants, which burn far hotter than our Sun. Blue giants can reach temperatures of 50 thousand degrees Celsius, releasing massive amounts of radiation.
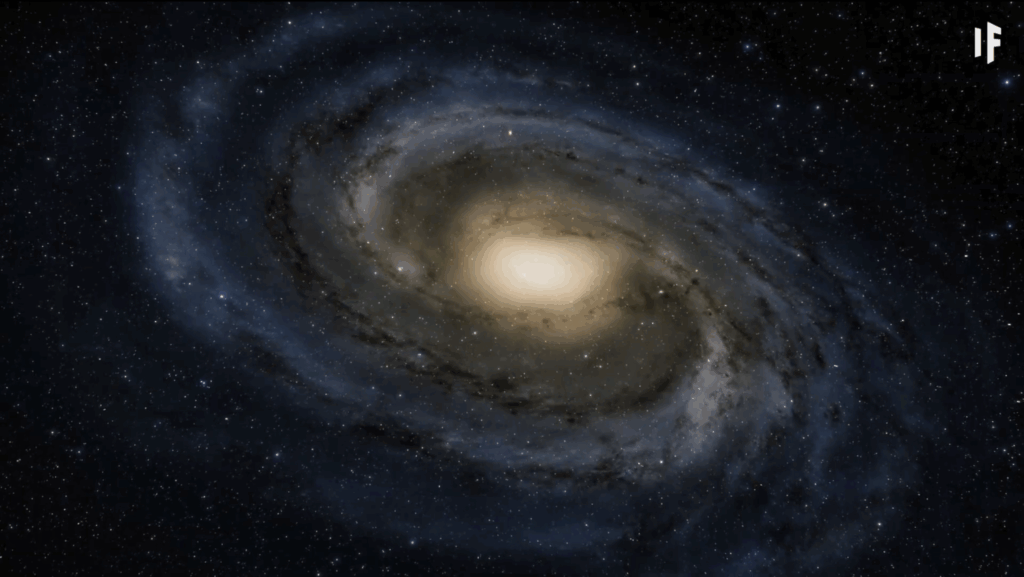

Still, the heat would only be felt near those stars, leaving most of space cold unless matter density increased across the board. The added starlight would also change how we see and measure the Universe, blinding our telescopes and altering astronomy forever.
5. Too Many Stars Could Wreck the Solar System
Placing massive stars too close to our Solar System would bring big problems. It might upset the gravitational balance that keeps planets in orbit. If stars with intense gravitational pull came near, Earth and its neighbors could be thrown off course or even pulled into another star.
The increased ultraviolet radiation would also be a health hazard, tearing into our ozone layer and increasing the risk of skin cancer. Bright skies might sound pretty, but the side effects of a crowded galaxy would be catastrophic. Entire planetary systems could collapse, and chaos would ripple throughout the Milky Way, endangering countless civilizations.
6. The Night Sky Would Never Be the Same
With more stars nearby, our night sky would change forever. The brightness would drown out the familiar constellations and make stargazing nearly impossible. Celestial wonders like the Milky Way’s faint band or distant galaxies would become invisible. Instead, the sky would glow constantly, disrupting natural cycles like sleep and animal migrations.
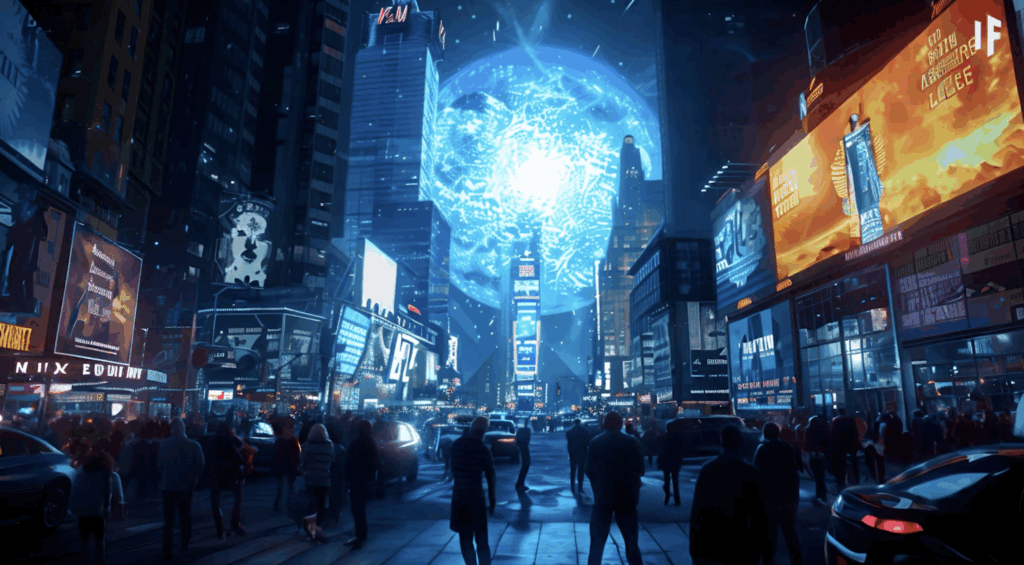

The peaceful, star speckled sky we take for granted would vanish, replaced by a permanent celestial glare. Nocturnal animals would struggle to adapt, and entire ecosystems could collapse from the constant exposure to artificial light.
7. Earth’s Future Would Become Extremely Uncertain
Whether space heats up from a fiery Sun or an overloaded galaxy, the consequences for Earth are dire. Our climate would spiral out of control, leading to supercharged weather, rising sea levels, and mass extinctions. The balance that allows life to thrive here is incredibly delicate. Even small shifts in space temperature could tip that balance permanently.

While space getting warmer might sound like science fiction, the truth is, our own warming planet is already showing us how fragile that balance can be. Unless we act quickly, we might experience a future that feels just as extreme and unforgiving as this hypothetical hot Universe.